Angiogenesis Is Driven by Which of the Following Growth Factors
Several growth factors including VEGF placental growth factor PlGF angiopoietin and angiostatins are produced within the villi and are involved in angiogenesis. NO plays an axiomatic role in mediating angiogenesis.

Angiogenesis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Advanced glycation end products-driven angiogenesis in vitro.
. VEGF is involved in many steps throughout the fracture healing cascade from initially being concentrated in fracture hematoma to the promotion of bone turnover during the final. Among the complex system of pro- and antiangiogenic factors the vascular endothelial growth factor system stands out as key mediator of tumor-initiated angiogenesis and as target of antiangiogenesis agents introduced in clinical practice. Each binds to transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptors displayed primarily by endothelial cells that are connected to intracellular signaling pathways.
Well known growth factors like platelet derived growth factor PDGF and the granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor GM-CSF have been implicated as endothelial cell growth factors 5354. 8182 The expression of VEGF is decreased in the villi of IUGR placentas. Dermal microvascular EC attachment through either α 1 β 1 or α 2 β 1.
Advanced glycation end products-driven angiogenesis in vitro. Whether other members of the VEGFR and ligand families such as VEGFR-1 and its ligand Placental Growth Factor PlGF can also contribute to developmental and pathological angiogenesis is. Transdifferentiation to endothelial cells or vascular mimicry has been reported through expression of endothelial markers.
Adaptive resistance -when block VEGF tumor cells rely on other factors to promote angiogenesis when you block one pathway tumors use other pathways 2. The angiogenic process consists of such multi-steps as degradation of basement membrane cell migration and proliferation and tube formation following activation of vascular endothelial cells by. 8 In such disorders leukocytes sustain inflammation by producing proangiogenic factors and stimulating angiogenesis.
It is a complex multi-step process that involves the migration and proliferation of capillary endothelial cells. Recently macrophages have been identified as key regulators of the host response to implanted materials. Angiogenesis is a complex process in which many growth factors such as VEGF 7 8910 angiopoietin 1 ANG1 basic fibroblast growth factor bFGF among many others are.
Angiogenic activity is induced by growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF basic and acidic FGF and PDGF. This is predominantly attributed to the activity of VEGFR-2 following binding of VEGF-A. These include nitric oxide NO endothelin-1 ET-1 tissue plasminogen activator tPA thrombospondin von Willebrand factor and prostaglandins.
Logically the use of pro-angiogenic growth factors has been the mainstay approach despite obvious limitations and modest success. The multifunctional growth factor scatter factorhepatocyte growth factor SFHGF and its receptor tyrosine kinase c-Met have emerged as key determinants of. Several factors that stimulate the.
80 VEGF and PlGF act as important paracrine regulators of decidual angiogenesis and autocrine mediators of trophoblast function. Angiogenesis one of the hallmarks of cancer has recently become the target of therapeutic approaches in oncology. This biological process is critical to both physiological and pathological processes such as wound healing and tumor growth.
Functional angiogenesis is a critical therapeutic goal in many pathological conditions. Angiogenesis is a complex process involving functional cooperativity between cytokines and endothelial cell EC surface integrins. 910 We have.
Up to 10 cash back In addition to production of pro-angiogenic growth factors ECM remodeling enzymes and chemokine signaling macrophages are known to drive angiogenesis through many other mechanisms. However angiogenic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis diabetic retinopathy solid tumor hemangioma and psoriasis are driven by persistent unregulated angiogenesis. Angiogenesis is regulated by an opposing balance of angiogenic and angiostatic factors.
This process is largely driven by the growth factor vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF whose levels are increased locally and systemically during fracture healing. Tip cells navigate toward hypoxic tissue. Perhaps not surprisingly angiogenesis is controlled and modulated by those factors manufactured by ECs.
The developing spout elongates by proliferation of endothelial stalk cells that trail behind the tip cell. Many researchers investigate the crucial role of a proangiogenic factor vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF in the process of tumor angiogenesis where the formation of new blood vessels carrying essential nutrients to the tumor cell becomes a critical factor for tumor growth. Angiogenesis the formation of new blood vessels plays a central role in a variety of physiological and pathological processes such as embryonic development wound healing and tumor growth.
In the cardiovascular system new blood vessel formation from preexisting vasculature in a process known as angiogenesis is driven by vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF binding to VEGF receptor 2 VEGFR-2 which promotes blood vessel development. Lymphocytes and monocytes might mediate inflammatorydriven angiogenesis which plays a key pathogenic role in several chronic inflammatory diseases including rheumatoid arthritis psoriasis and IBD. Intrinsic non-responsiveness -tumors can use other pathways to create tumor - all driven by observation not clear which is which.
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor VEGFR mediated signalling drives angiogenesis. Induction of the growth and tube formation of human microvascular endothelial cells through autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor. Endothelial cells exposed to the highest VEGF-A concentration become tip cells.
The tip cells lead the developing sprout by extending numerous filopodia. In this study we investigated the mechanisms through which the α 1 β 1 and α 2 β 1 integrins support angiogenesis driven by vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF. Alternatively it is possible that still other as yet uncharacterized factors play a crucial role in angiogenesis.
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing microvasculature.

Difference Between Angiogenesis And Neovascularization Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Role Of Cscs In Melanoma Growth Metastasis And Angiogenesis Cytokines Download Scientific Diagram
Ijms Free Full Text Exosomes In Angiogenesis And Anti Angiogenic Therapy In Cancers Html
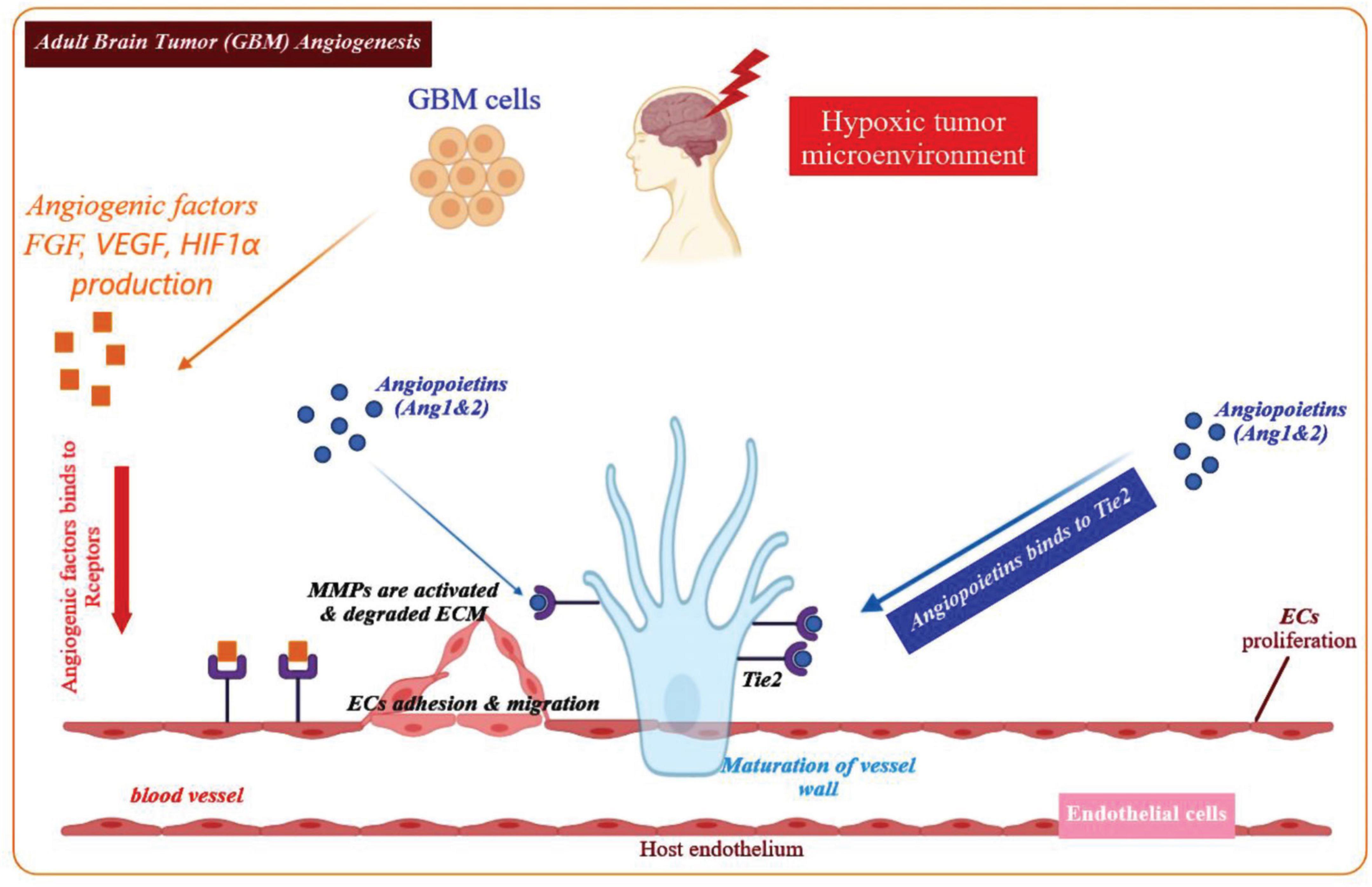
Frontiers Roles Of Non Coding Rnas And Angiogenesis In Glioblastoma Cell And Developmental Biology
Cells Free Full Text Trends And Challenges In Tumor Anti Angiogenic Therapies Html
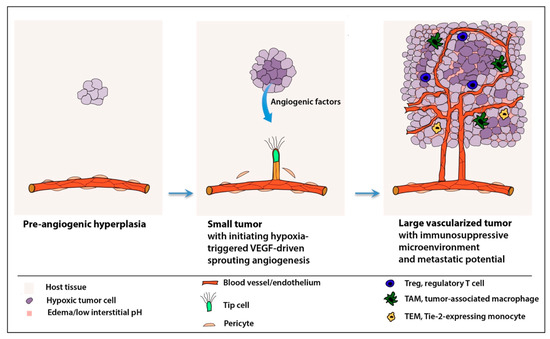
Cells Free Full Text Trends And Challenges In Tumor Anti Angiogenic Therapies Html

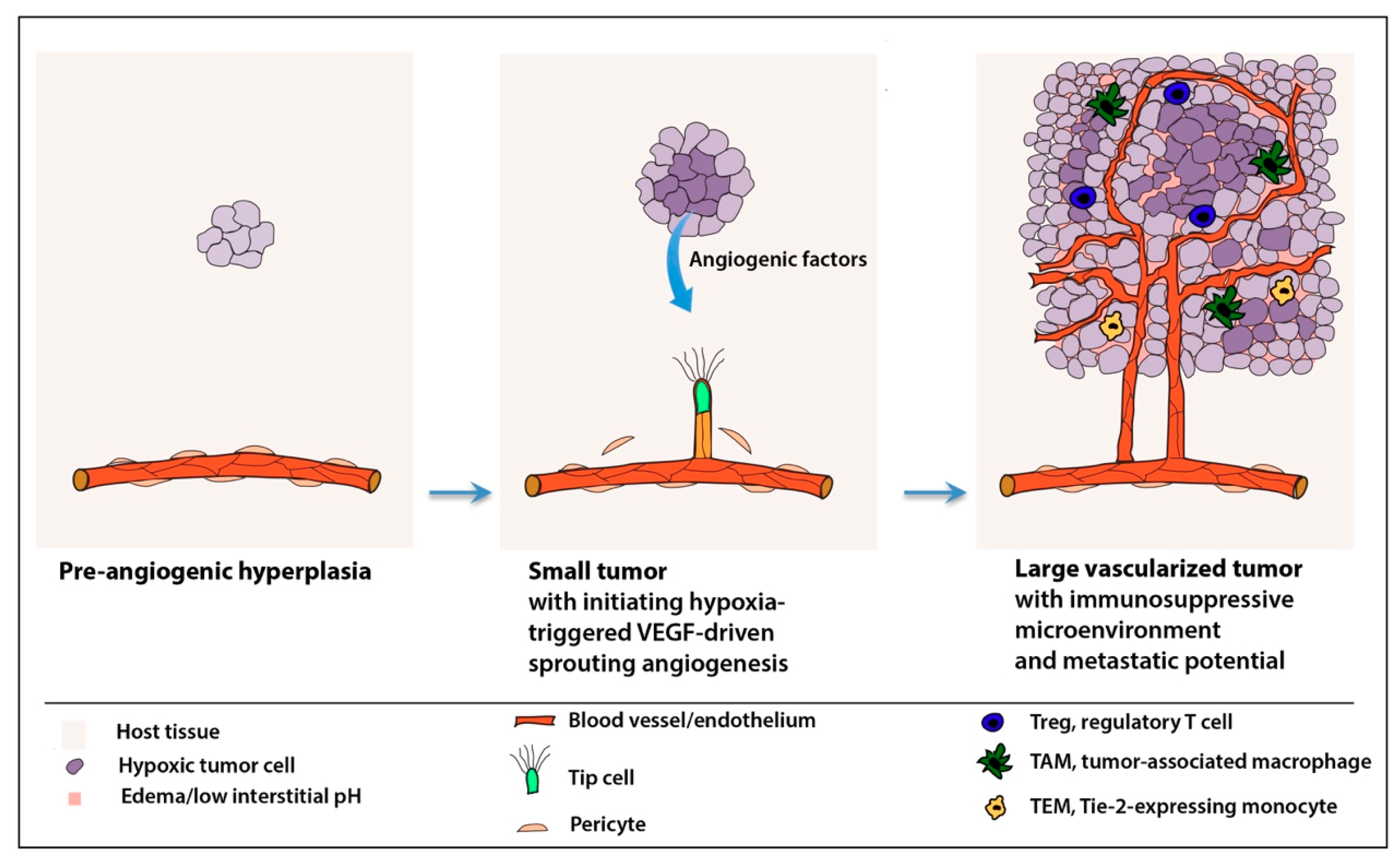
The Angiogenic Cascade During The Process Of Angiogenesis Stable Download Scientific Diagram
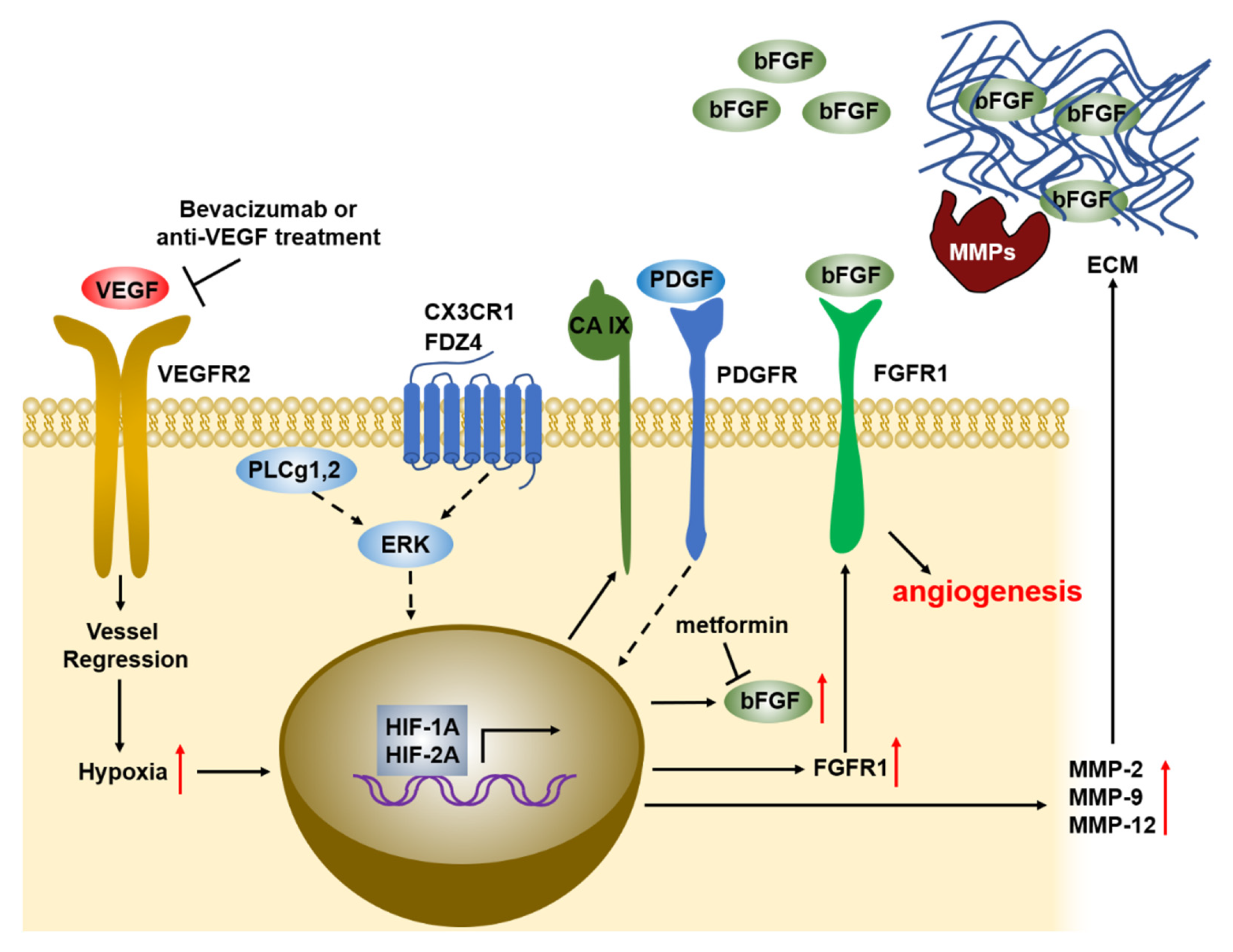
Cancers Free Full Text Role Of Bfgf In Acquired Resistance Upon Anti Vegf Therapy In Cancer Html

Agrin Mediates Angiogenesis In The Tumor Microenvironment Trends In Cancer

Angiogenesis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
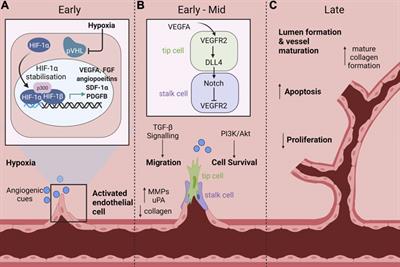
Frontiers The Role Of Mir 181c In Mechanisms Of Diabetes Impaired Angiogenesis An Emerging Therapeutic Target For Diabetic Vascular Complications Pharmacology
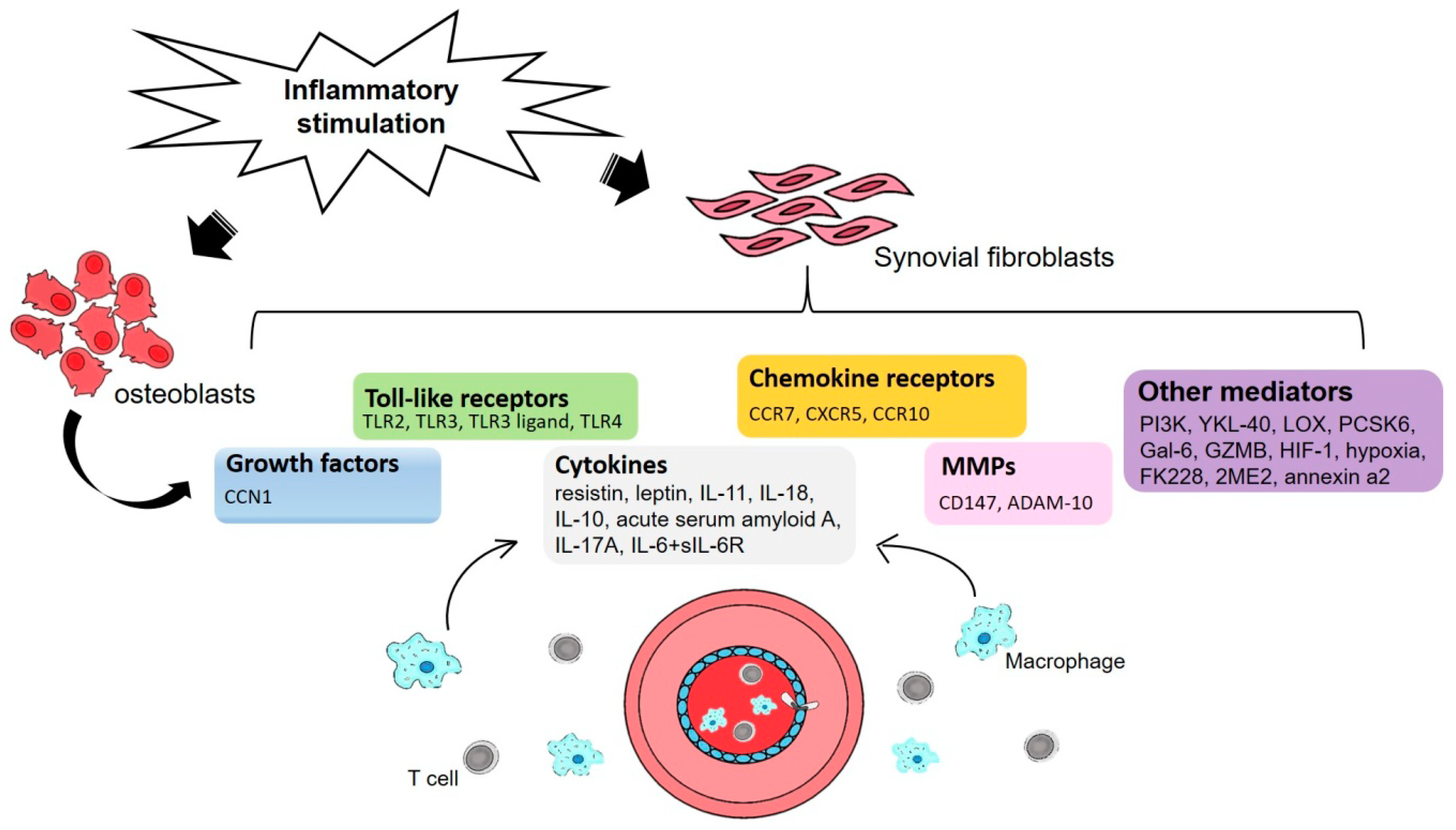
Ijms Free Full Text Implications Of Angiogenesis Involvement In Arthritis Html
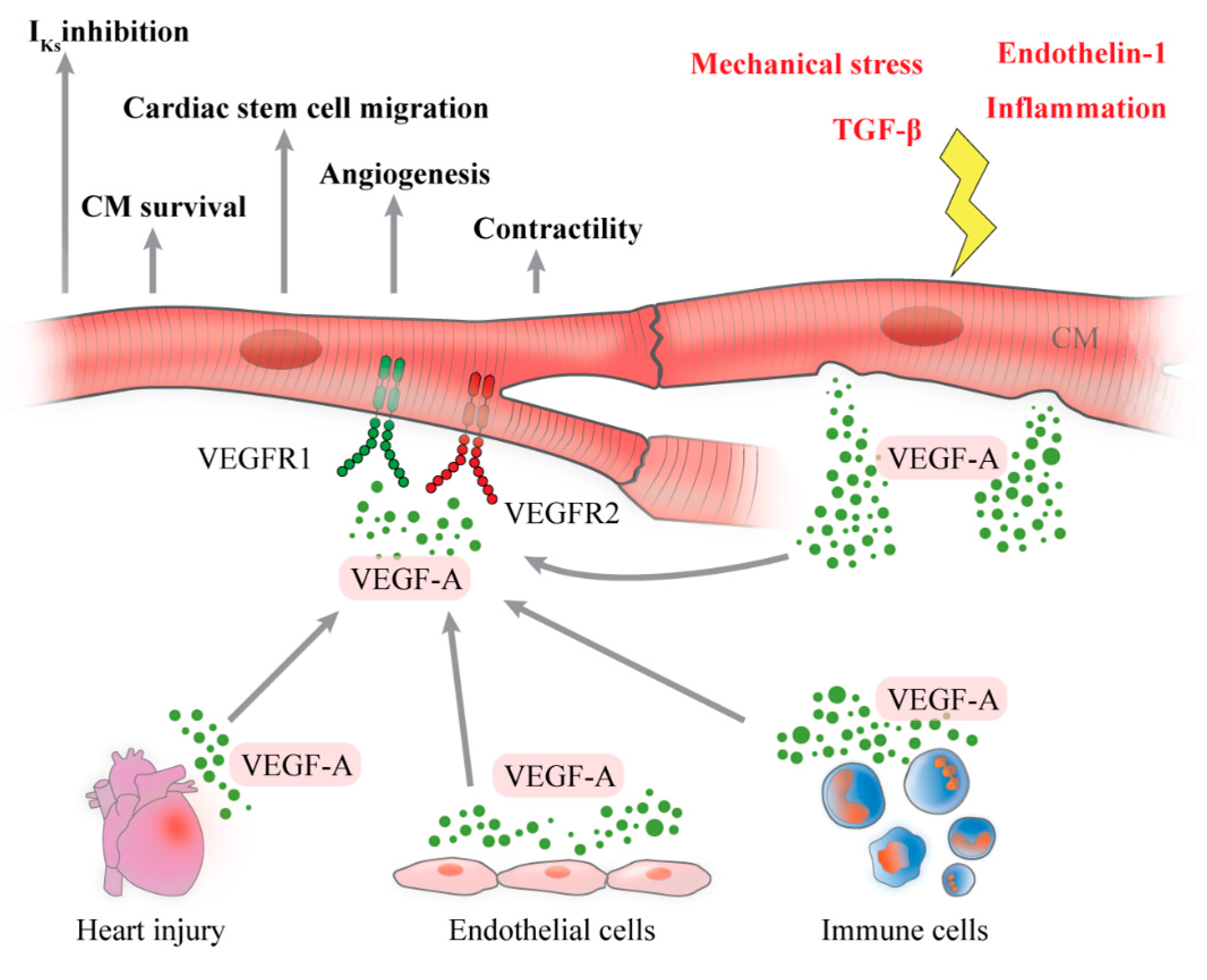
Ijms Free Full Text Vegf A In Cardiomyocytes And Heart Diseases Html

Biomolecules Free Full Text Anti Angiogenic Effects Of Phytochemicals On Mirna Regulating Breast Cancer Progression Html

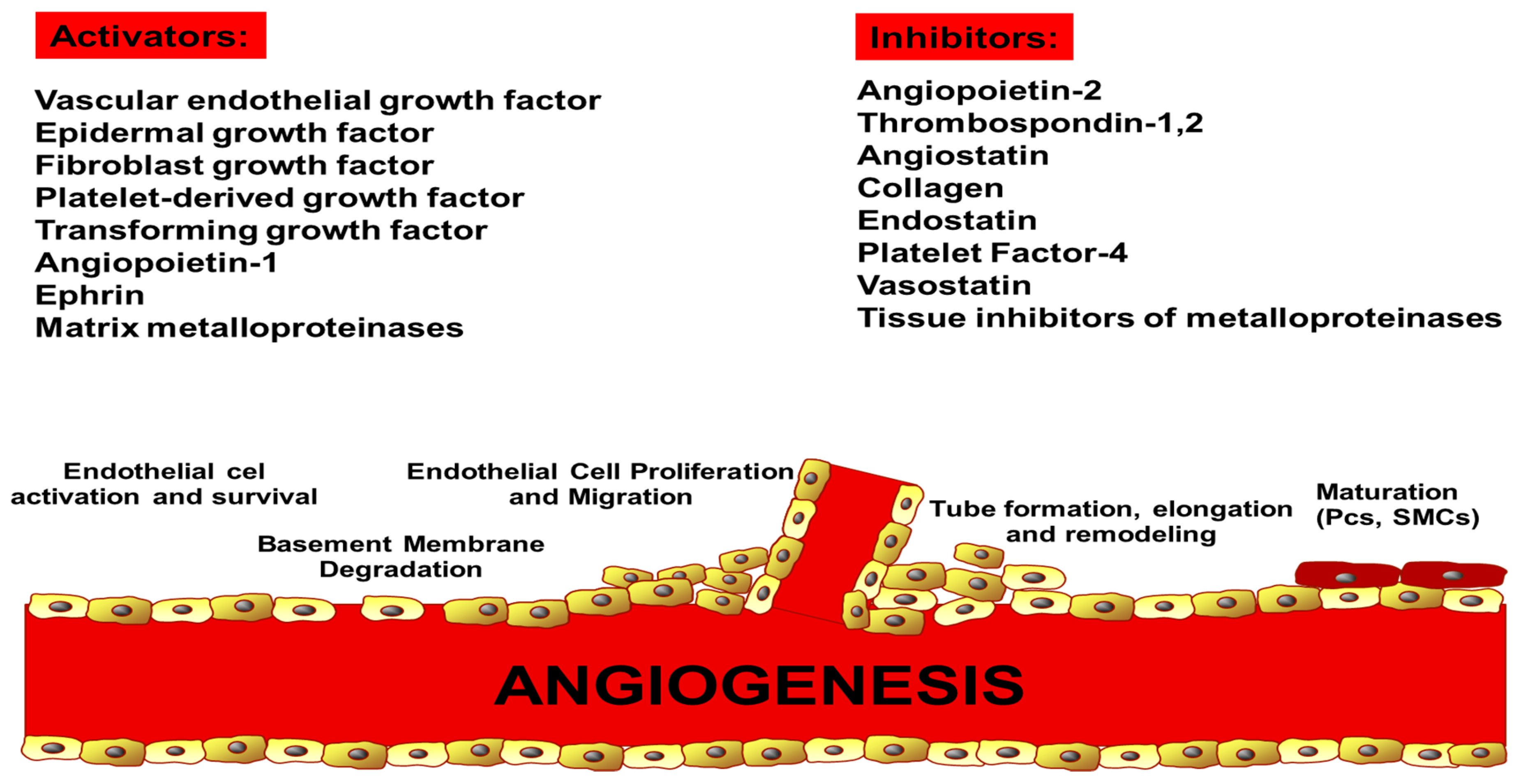
Promoters And Inhibitors Of Angiogenesis A Balance Of Pro And Download Scientific Diagram
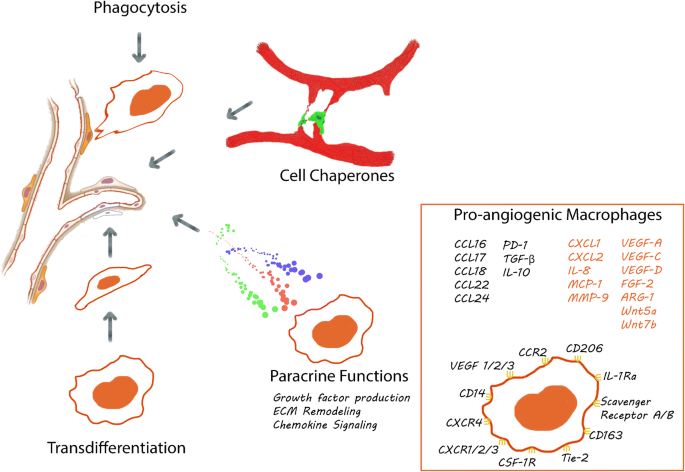
Beyond Growth Factors Macrophage Centric Strategies For Angiogenesis Springerlink

Tumor Angiogenesis A New Source Of Pericytes Current Biology
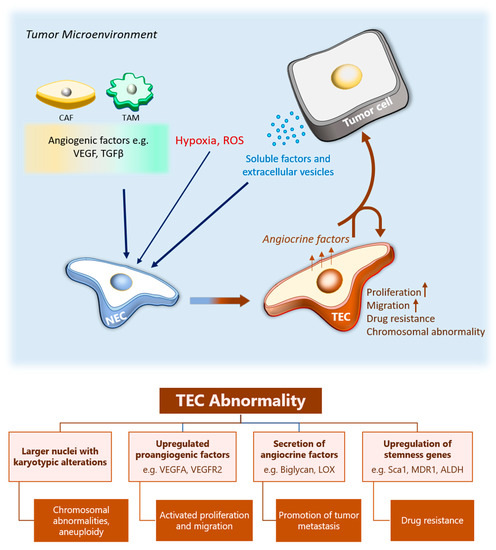
Cancers Free Full Text Tumor Endothelial Heterogeneity In Cancer Progression Html

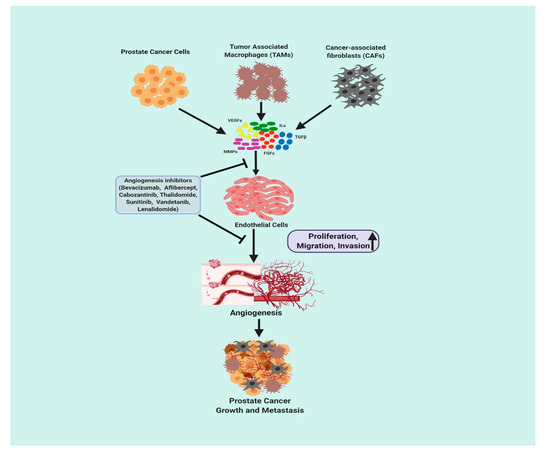
Cancers Free Full Text Angiogenesis Inhibition In Prostate Cancer An Update Html
Comments
Post a Comment